Gone the days that 3D printing was science fiction. 3D printing has entered our daily lives and it is here to stay. By using 3D printers, people are able to create/develop unimaginable things.
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by building them layer by layer using a variety of materials, such as plastics, metals, and ceramics. It has gained popularity in recent years due to its ability to quickly and accurately produce complex parts and prototypes, and its potential to revolutionize manufacturing and supply chains.
One of the main benefits of 3D printing is its ability to produce complex parts with high accuracy and precision. Traditional manufacturing methods, such as injection molding and CNC machining, can be time-consuming and expensive, especially for small batches or custom parts. 3D printing, on the other hand, allows for rapid prototyping and the production of small batches of parts at a lower cost.
Another benefit of 3D printing is its ability to reduce waste and improve sustainability. Traditional manufacturing processes often generate a significant amount of waste, as excess material is removed to create the final product. 3D printing, on the other hand, only uses the material that is needed to create the final product, reducing waste and the environmental impact of manufacturing.
Additionally, 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize supply chains and logistics. With 3D printing, it is possible to produce parts on-demand, reducing the need for large inventories and long lead times. This could potentially lead to a more flexible and responsive supply chain, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
However, 3D printing also has some drawbacks. One of the main limitations of 3D printing is the limited range of materials that can be used. While the range of materials is constantly expanding, there are still many materials that cannot be used in 3D printing. In addition, the quality of 3D printed parts can be lower than that of parts produced using traditional manufacturing methods, especially for high-stress or load-bearing parts.
Another drawback of 3D printing is the time required to produce parts. While 3D printing can be faster than traditional manufacturing methods for small batches or complex parts, it can be slower for large batches of simple parts. Additionally, the cost of 3D printing can be high, especially for larger parts or those made from exotic materials.
3D printing is a promising technology that has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing and supply chains. While it has some limitations, it offers many benefits, including the ability to produce complex parts with high accuracy, reduce waste and improve sustainability, and enable on-demand production.
Bellow is a list of cool items created by using 3D printers.
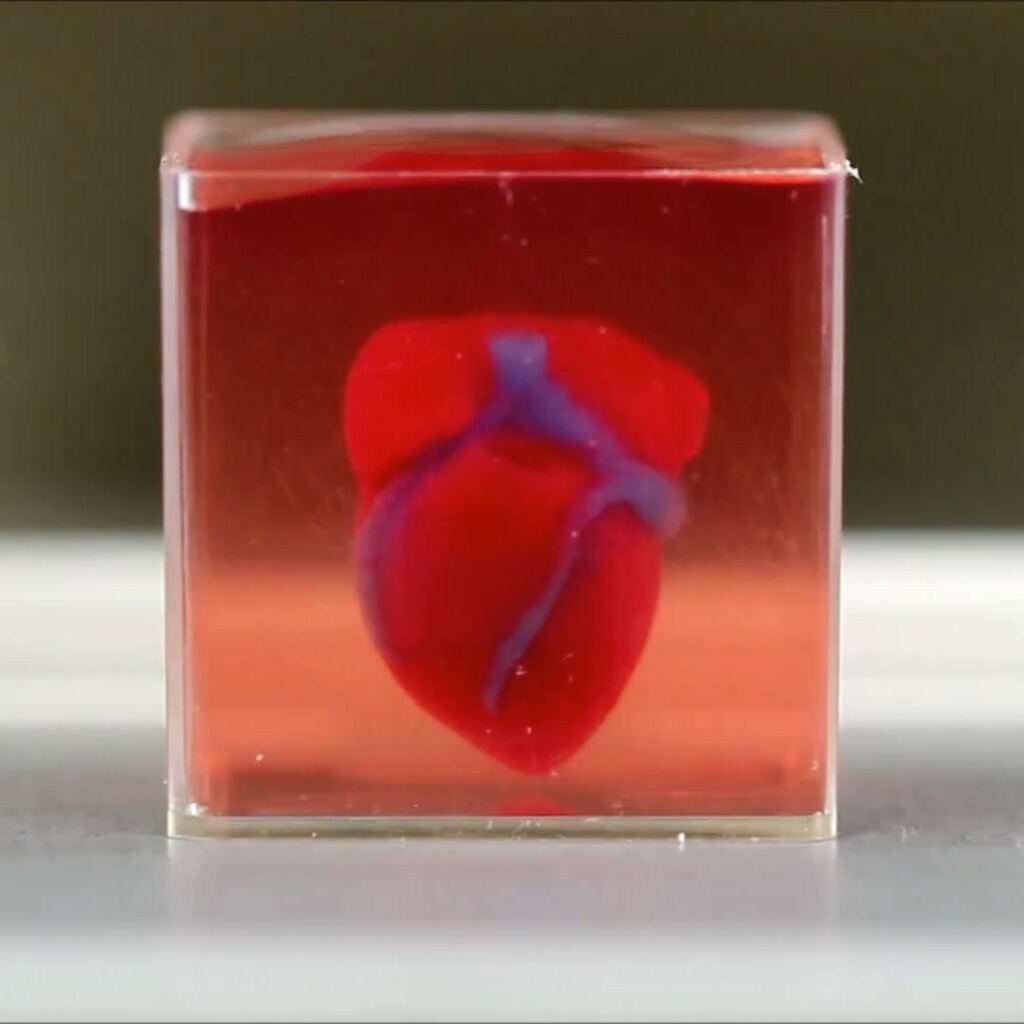
1. 3D printed organs
When we talk about 3D printed organs, we don’t mean only printing some kind of robotic hand like Luke Skywalker’s one, but we really mean real 3D printed organs.
3D printing is going to change the health industry. In the near future, your doctor might be able to 3D print your missing ear or other missing parts of your body. No, it is not science fiction anymore. Scientists have already succeeded bioprinting ear made from children’s own cells. Also, scientists at Tel Aviv University (TAU) have succeeded bioprinting the world’s first 3D vascularized engineered heart. They achieved that by using a patient’s own cells and biological materials.
2. A 3D printed boat
In October 2019, the University of Maine revealed the world’s largest 3D printed boat. The boat had a length of 25 feet (7.62 meters) and weighted almost 5000 pounds (2.25 metric tones). The boat named 3Dirigo, was 3D printed with the additive manufacturing process from a mixture of plastic and wood cellulose.
The team of the project was awarded 3 world records: 1) the largest 3D printed solid part, 2) the largest 3D printed boat and 3) the largest 3D printer. 3Dirigo took almost 72 hours to be printed. Bellow you can see a time-lapse of the world’s largest 3D printed boat.
3. 3D printed houses
Lately, 3D printed houses are popping up all around world like mushrooms. The 3D printing technology has advanced so much that it is now able to build houses in a single day.
An example of it comes from the construction company Apis Cor. Apis Cor was able to 3D print a house in 24 hours with a cost a bit more than $10,000. The house has an area of 400 square feet (38 square meters). The main components of the house’s structure were fabricated on site by using concrete. This dramatically cut down costs on transportation and assembly. It is predicted to be durable enough to last up to 175 years.
4. Violins
3Dvarius, is one of the only companies in the world that succeeded producing commercial grade 3D printed violins. It started as personal project and challenge. That was to design an electric violin which wouldn’t weigh more than a classic, wooden acoustic one.
The violin got printed with the Stereolithography process. This process is using UV laser to polymerize liquid resin which is photosensitive. The violin made its debut in a Kickstarter campaign where 3Dvarius pledged €53,231 (around $63,294) out of their €50,000 initial goal.
After their successful Kickstarter campaign, 3Dvarius currently has a series of 4 different electric violins in their product line up.

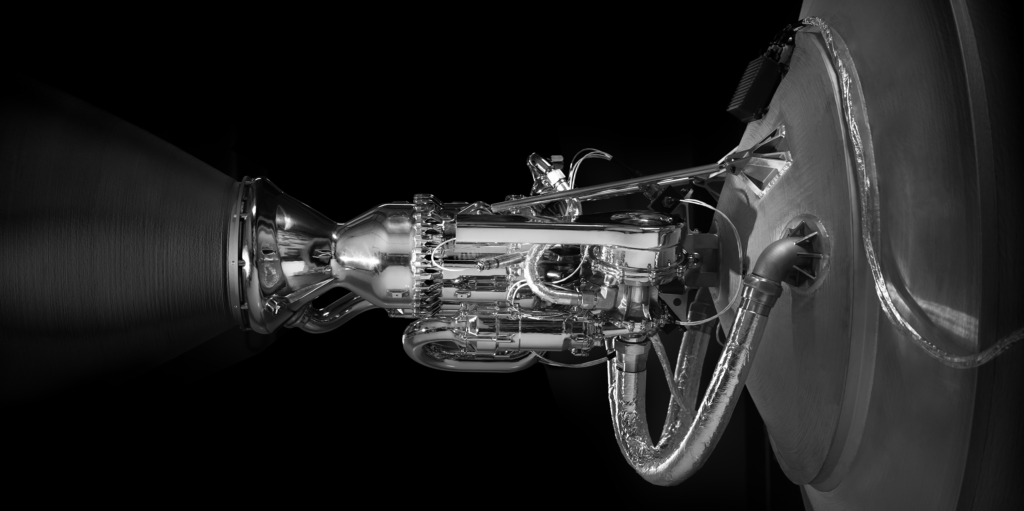
5. Rockets
3D printing allows the fabrication of large components with highly complex internal structure that otherwise it would be time consuming. The ability to significantly reduce the time and the associated costs of the fabrication of mechanical components is the driving force for various manufacturers that start fabricating their components by using the 3D printing technology.
Relativity Space, is one of such companies to embrace the usage of 3D printing. Their Terran 1 rocket is made by a proprietary 3D printed alloy. 3D printing, allows them to reduce the parts count of the rocket by 100x, simplifying the design of it and lead times. The Terran 1 rocket is consisted of 730 parts and it is much more simple to fabricate compared to rockets from other manufacturers that are made from more than 60,000 parts.
6. 3D printed cars
Lately, there have been done huge efforts by car manufacturers to produce 3D printed cars. The Czinger 21C is a 1,233bhp hypercar where large sections of its chassis are 3D printed. An other example is the Strati, an electric car developed by Local Motors. The car was manufactured during the 2014 International Manufacturing Technology Show in Chicago, Illinois.
This was done by using a large scale 3D printer. It took just 44 hours to print and it was followed by three days of milling and assembling. The completed car was first test-driven on September 13th, 2014. Depending on the battery packs of the car, the range of it can be from 100 to 120 miles (160 to 190 km) and can achieve top speeds of 40 mph (64 km/h).
Currently, we do not have any news about Strati. As such, we believe that Local Motors didn’t continue the development of it.





Comments
Loading…